
The female form of this title is empress and can be divided into two types, namely empress regnant, which is a woman who rules the empire on her own behalf or empress consort who is the wife of the emperor. The emperor’s territory is called the empire. This title comes from the ancient French empereor, from the Latin imperator) which originally meant “commander” in the Roman Republic. The emperor is the highest level of nobility and monarch in the rank of European nobility. However, several levels commonly known in the European continent are: emperor (emperor), king (king), duke (duke), marquess, count or earl, viscount, and baron. Some titles in a country sometimes do not have their equivalent in other countries and languages, even though they are still within the scope of the European continent. These ranks and titles were usually conferred by the emperor or king who was the leader of the aristocrats, and in many cases these titles could be passed on to their descendants.Įach region in Europe has its own level of nobility which has several differences from one country to another. These aristocrats had different ranks, which also impacted the amount of power they held. Several regions and territories within a large monarchy (empire or kingdom) are usually administered and led by aristocrats who have autonomous powers, similar to a federal republic system that gives each regional leader the authority to manage his own territory without too much interference from the center.

In medieval Europe and earlier, an empire or empire usually did not have a central government. You can se below the European noble ranks in Latin, French, German, Russian and Spanish. This European noble ranks are written in English.

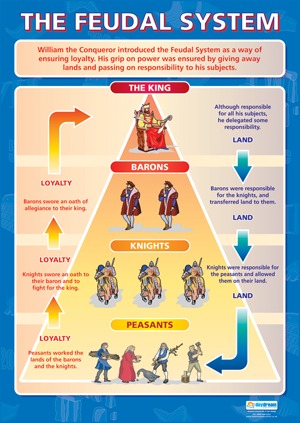
Even so, there are some differences in each period and each region. The European noble ranks among the European society has its roots in the Late Ancient and Middle Ages. The biggest problem was that since some special duties were assigned to the different classes, people of the specified class were not allowed to take up the desirable jobs.īy the beginning of the 19 th century, as a result of many revolutions, the feudal system also saw its end.Aristocracy, Europe, UK European Noble Ranks The lower class was treated very badly and rudely by the lords. There were also some vital problems in the feudal hierarchy system that poor were becoming poorer and rich were becoming richer with the passage of time. The protection of the land was among the duties assigned to the vassals. A fealty oath was taken to reinforce all the promises made during the royal homage. The process includes having a contract which states to provide services to the lord, even fighting at the command of the lords and in return lord promised not only to provide land but also to protect the vassal form various external forces. Before granting the fief to the lower class (vassals) a ceremony called commendation ceremony used to be held accompanied by the oath of fealty and a royal homage. The lords granted their lands to these vassals and in return ask for rent and some services. Vassals/ Lower Class: The fief land was allocated to lower class that was termed as vassals.Lords were considered the upper class and got special privileges as compared to the lower class. The land which was rented to the lower class was termed as a fief. A lord distributed the grants of lands to the people at lower class known as vassals to get, in return some special services along with the rent of the land granted.

A lord can be termed as a master, ruler or a chief.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
